Stereotactic Radiosurgery: radiation therapy (e.g., gamma knife, LINAC) used to treat brain tumors and other conditions.
Gamma Knife
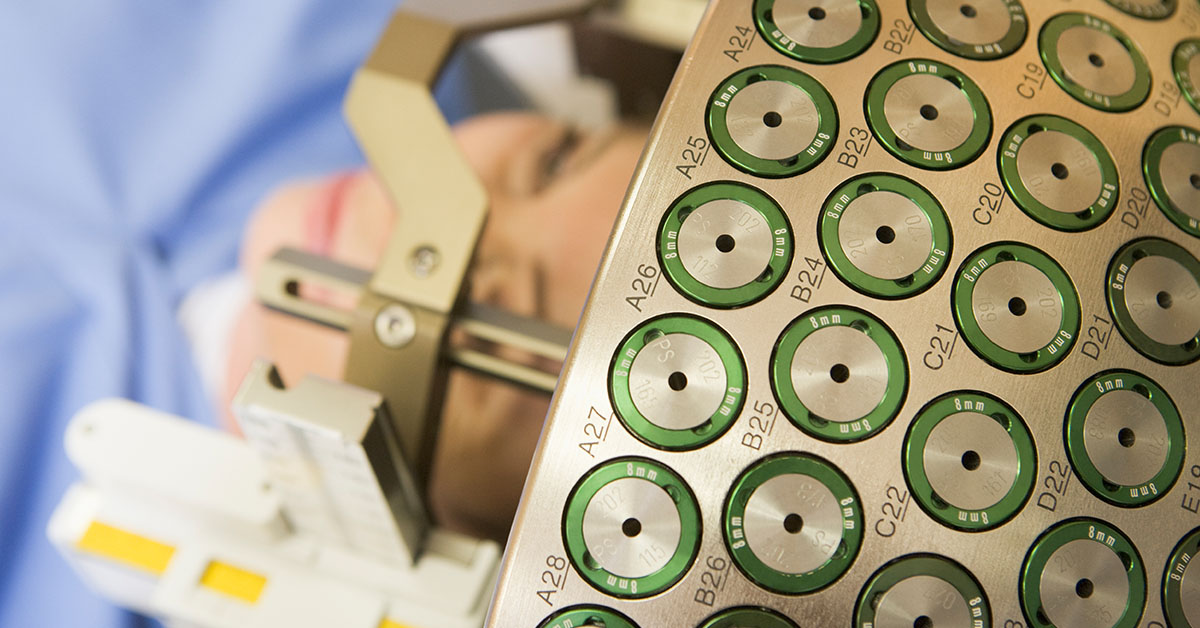
What is Stereotactic Radiosurgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is typically a one-session treatment but sometimes it can be a staged procedure. One-session treatment delivers a high dose of radiation in a single, one-day session. This session can last from less than one hour to four hours, depending on the size and location of the affected area. A staged treatment (known as Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery of FSR) delivers the total dose of radiation in several smaller doses on different days. Despite its name, stereotactic radiosurgery is not a surgery in the conventional sense. It is a treatment, not a surgical procedure, because no incision is required.
Gamma knife and Linear Accelerator (LINAC) are two specific types of stereotactic radiosurgery.
Who needs radiotherapy?
Patients who have abnormal blood vessels in their brains may need this treatment. Examples of abnormal vessels include arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), trigeminal neuralgia and arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). It's also utilized for patients with brain tumors, acoustic neuromas, pituitary tumors, and brain metastases.
Radiotherapy is used when tumors are deep within the brain and difficult to remove via surgery. It's suggested for patients who cannot have surgery (e.g., the elderly, or those too weak or sick). Also, it is can be used after conventional surgery to treat any remaining abnormal tissues.
How is radiotherapy performed?
The following steps outline a stereotactic radiosurgery procedure:
- Computed tomography (CT) scans or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) will be used to determine the precise location of the tumor or abnormality.
- The results of these scans are entered into a computer that will help determine the appropriate dosage of radiation and configuration of the x-ray beams.
- While the patient is lying down, a lightweight frame will be attached to their head. The frame helps stabilize the head during the treatment.
- This bed slides into the radiosurgery machine and the head frame is securely attached to a helmet in the machine.
- The beams of radiation are targeted on the specific area and released . The patient cannot feel this radiation.
- After the delivery of the radiation is complete, the head frame is removed.
What happens after radiotherapy?
The patient may be given medication if they experience nausea or headache.
After an hour, most patients can go home, and is free to drink and eat. However, some patients may need to stay in the hospital overnight for monitoring.
Most patients resume their normal routines the day after radiosurgery, unless there are complications (e.g., swelling).
