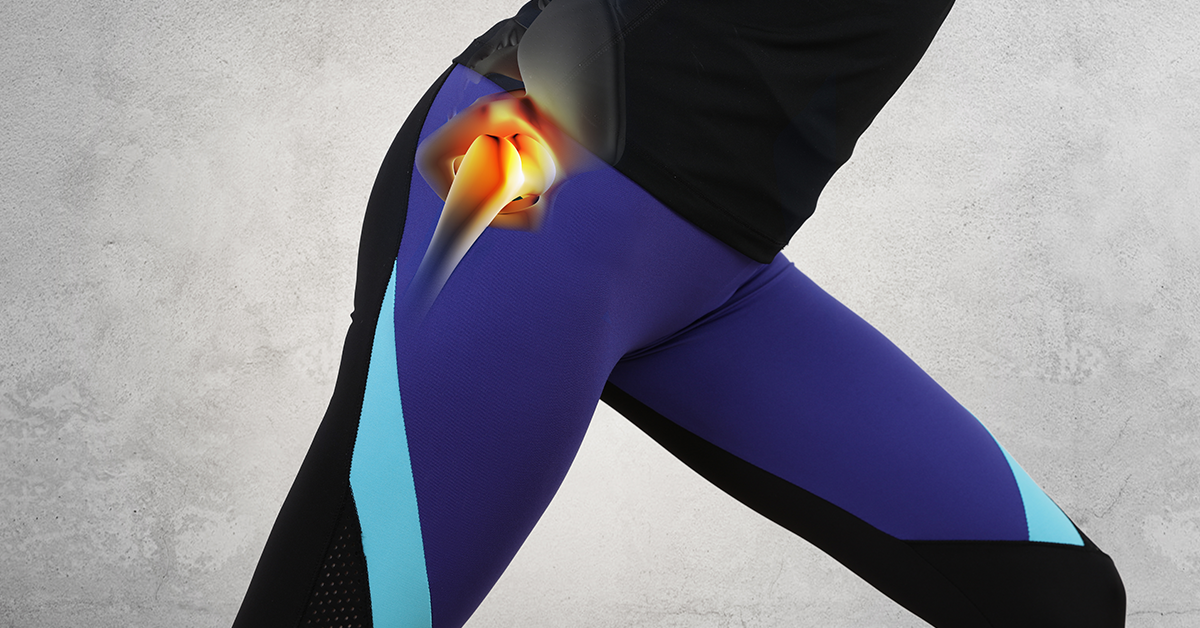
What Does “Bone-on-Bone” Contact Mean in the Hip?
The term "bone-on-bone" contact is often used in discussions about joint health, particularly in relation to arthritis. But what does it mean when doctors say there's "bone-on-bone" contact in the hip?
In a healthy hip joint, the ends of the bones are covered by a smooth, slippery tissue called cartilage. This cartilage acts as a cushion and allows the bones to glide smoothly against each other, enabling pain-free movement. However, when this cartilage wears away or is damaged, the bones can no longer glide smoothly. Instead, they start to rub directly against each other. This condition is referred to as "bone-on-bone" contact.
Bone-on-bone contact in the hip is a hallmark of advanced osteoarthritis. As the cartilage deteriorates, the friction between the bones increases, leading to pain, inflammation, and decreased mobility. This condition can make everyday activities such as walking, bending, and even sitting very painful.
Several factors can contribute to the development of bone-on-bone contact in the hip:
- Aging: As we age, the wear and tear on our joints can lead to cartilage breakdown.
- Injury: Past injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can damage the cartilage and accelerate its deterioration.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoarthritis can increase the risk of developing bone-on-bone contact.
- Overuse: High-impact activities and repetitive motions can wear down the cartilage over time.
Symptoms of bone-on-bone contact in the hip include chronic pain, stiffness, swelling, and a reduced range of motion. These symptoms can significantly affect your quality of life, making it difficult to perform daily tasks and enjoy activities you once loved.
If you suspect you have bone-on-bone contact in your hip, it's important to seek medical advice. A doctor can diagnose the condition through physical examinations, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, and discussing your symptoms and medical history.
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition. They can range from conservative approaches like physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes to more advanced interventions like injections or hip replacement surgery. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Understanding what bone-on-bone contact means and recognizing the symptoms can empower you to take proactive steps in managing your hip health. If you're experiencing persistent hip pain and stiffness, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
