Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy is a complication that can affect up to half of older patients with type 2 diabetes
What is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy?
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy, or DPN, is a clinical condition that can affect up to half the older patients who suffer from type 2 diabetes. DPN is an important and common complication of diabetes. Careful examination and meticulous blood sugar control can help patients manage the symptoms effectively.
What causes Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy?
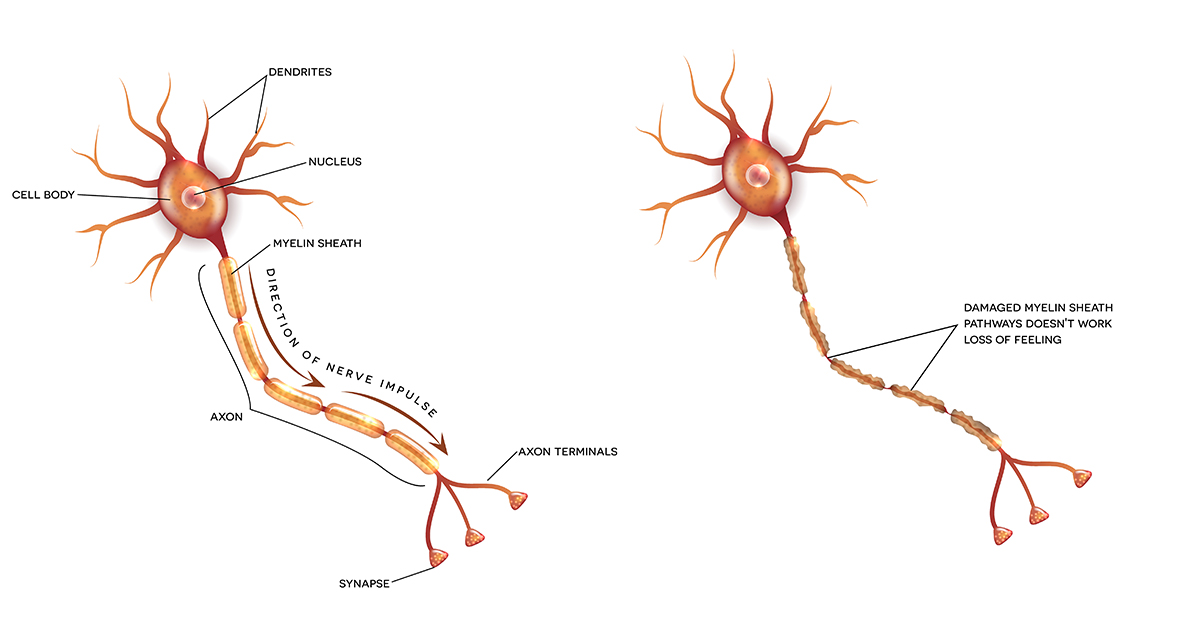
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy refers to a clinical condition where there is abnormal function of the nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord due to underlying diabetes. It forms one type of neuropathic conditions that occur in diabetes patients.
There are two types of DPN. Acute sensory neuropathy is one that occurs suddenly in patients in whom the blood glucose levels are unstable such as diabetic ketoacidosis, and it usually resolves by itself once the blood glucose levels are normalized. Chronic sensorimotor neuropathy is the more common type which develops over a period of time and is the type of DPN that is often seen when type 2 diabetes is diagnosed.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Patients who suffer from DPN can have a plethora of symptoms. Many patients have no symptoms for quite a while. Pain is the most common symptom that is usually seen in the lower legs and hands. The pain is typically described as burning pain or like a knife is being driven through, and some patients have also reported an electric shock sensation before. The legs may also feel numb and patients may experience a tingling sensation. The distribution of symptoms is often called glove and stocking distribution.
DPN is diagnosed from a clinical history of diabetes and clinical signs on examination. Nerve conduction studies may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. It is essential to accurately diagnose DPN as there can be other causes of it that are treated differently. These need to be ruled out before hand, so certain special blood tests may need to be performed first.
How is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy treated?
There are a number of different ways DPN may be treated. These can include:
- Home measures: Wearing comfortable footwear and maintaining foot hygiene are important. The loss of sensation in the feet means patients may not feel pain if they suffer from an injury. Simple painkillers are effective in managing pain, though stronger painkillers may be required.
- Controlling blood sugars: This is one of the most important steps in managing DPN. Your doctor will provide you with the advice and treatment that you need, but it is also up to you as a patient to monitor your blood sugar at home and watch the amount of sugar you eat. Studies have shown that blood sugar levels that are poorly controlled can increase the amount of pain patients experience as a result of DPN.
- Medical management: This includes pain killers such as tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsant medication and even opioids analgesics. Physical therapists can provide treatments such as electrical nerve stimulation and laser treatment to help improve nerve conduction and reduce pain.
